MediChain - The Medical Big - Data Platform - Saving Lives With Blockchain
website : https://medichain.online/
MediChain is a Medical Big-Data Platform. It enables patients to store their own information off chain in a proper geographic area, and offer access to specialists and authorities anyplace paying little respect to the payer system or EMR utilized. MediChain is exceptional in therapeutic records in as much as it doesn’t simply give a patient arrangement yet use the estimation of the information as large information
MediChain gives patients responsibility for claim therapeutic information. MediChain is a conveyed record for patient’s therapeutic information. It enables patients to store their own particular information secury and offers access to masters anyplace paying little mind to the payer system or EMR (Electronic Medical Record) utilized. At whatever point any information is assembled about a patient, by gadget or therapeutic expert, apportioning a remedy or even buy of a non doctor prescribed drug the patient (through an application) or the gadget get an opportunity to have a reference or “pointer” added to an Ethereum blockchain — a decentralized advanced record. So the blockchain is a record to capacity and it contain the hashes that approve the offchain information. ‘Rather than installments, this blockchain biological community records basic medicinal data offchain, filed by a basically upright cryptographic database, kept up by a system of PCs, that is open to anybody running the product and has the patient’s authorization to get to the particular cryptographic keys. Each time when a specialist sign on the blockchain (or the patient logs for themselves with their smartcard, giving them control of their own information) would turn out to be a piece of a patient’s offchain record, regardless of which electronic framework the specialist was utilizing — so any guardian could utilize it without stressing over inconsistency issues. Thusly, blockchain innovation can give patients more control over their data and streamline the trading of medicinal records secury, shield delicate information from programmers and ensure that patients get advantage from sharing data. A custom-fabricated “human services blockchain” will proclaim a broad unrest in medicinal records at a far more profound level than has been hypothesized past.
The Plan
Working from our current demonstrator, MediChain framework will be produced on an Ethereum system with offchain information put away in secure mists in proper locales. It will at first be propelled in a joint effort with various restorative specialities, for example, epilepsy and rheumatology and particular demonstrative gadgets. The following stage will develop the chain information distribution center through an open access API and restorative organizations. MediChain will then be made publically accessible through the API and through accomplices for information obtaining. At that point a trade will been produced to permit secure controlled anonymized information access to understanding information.
Medical records are any records that document the pertinent facts of a patient’s life and health history, including past and present illness (es) and treatment(s), written down by the health professionals handling the patient’s care. The records must be compiled in a timely manner and contain sufficient data to identify the patient, support the diagnosis or reasons for the healthcare encounter, justify the treatment, and accurately document the results. As such, they are the visible evidence of the hospital’s clinical activities and accomplishments. It contains sufficient information to identify the patient, support the diagnosis based on history, physical examination and investigations, justify the professional management given, record the course and results thereof, and ensure the continuity of care provided by practitioners and other healthcare workers to that particular patient. Medical records are either in paper form or electronic form.
A paper-based medical record is a systematic collection of patient’s personal information and health history which is documented or written on paper form . Traditionally, active records are usually housed at the clinical site but older records (e.g those of the deceased) are often kept in separate facilities.
Electronic Medical Record (EMR) is a computerized medium that contains clinical information as recorded in a patient’s record. This is only restricted to clinical information which refers to patient data which includes, for example, diagnoses, allergies, prescriptions, etc. Some EMRs include an additional module, or component, for registering patients’ demographic information.
To sum it up, hospitals keep medical records for a number of reasons, which includes:
- for communication purposes while caring for the patient
- for continuity of patient care over the course of the patient’s life
- for evaluating patient care
- for medico-legal purposes
- for use as a source of health statistics
- for research, education and planning purposes.
- medical record is compiled primarily to assist physicians and other health care professionals in treating patients.
- The record contains information on past and present conditions and treatment, family history, diagnosis, progress notes, consultation reports and laboratory tests. It may also include opinions on the condition and care of the patient.The record provides for continuity of patient care and maintenance of an optimal standard of care. Secondary uses for the information contained in the medical record include epidemiologic studies, research, education, remuneration for services rendered and quality assurance.
Now, Having given the basic meaning of medical records, what challenges are encountered while keeping these records
The sensitivity of medical records has brought several challenges to managing institutions. The commonest relates to storage, access, safety and security. Hospitals which use primarily manual based medical records systems experience storage problems. Access to medical records is another challenge that users and custodians face. Sometimes there is conflict on the ownership and the right of access to a patient record. The US Fair Health Information Practice Act of 1997 has tried to reduce this friction by mandating a healthcare provider to allow individuals to examine their medical records and it also has provision for a civil and criminal penalty for failure to abide by this requirement.
The safety and security of medical records is a challenge to personnel in-charge of patient records. There were numerous instances where case notes were not kept in secure conditions. In a number of examples, it would have been easy for unauthorized persons to have had access to case notes either from open libraries or from other uncontrolled areas. Case notes, for instance, were found unattended to in out-patient clinics and were sometimes left in clinic areas overnight because the medical records department had closed. All users of case notes (doctors, nurses, medical secretaries, ward clerks, medical records staff and others) should be aware of the importance of security.
Unattended computer terminals, particularly if left logged on, are another risk as are fax machines and inadequately protected and controlled computer networks The challenges of managing medical records are closely linked to the abuse of patient information. When medical records are not properly managed, without proper security measures, they can be misused, which can lead to possible violations of privacy and confidentiality of medical records. There are several misuse of medical records and the confidentiality of medical records is threatened in many different ways. Most news worthy is the misappropriation and disclosure of medical records for financial gain or to cause harm or embarrassment.
The threat of abuse of medical records manifests, not just in unauthorized users, but in those authorized to access files as well. Often, confidentiality is breached through legally sanctioned activities such as billing procedures conducted from remote locations as well as casual or careless conversations among medical professionals in hospital elevators.
It is also important to note that the misuse of medical information found in medical records is not only manifested in paper-based records, misuse can also occur in electronic based records. Electronic tools such as the Internet, electronic mail, digital imaging and telemedicine are now indispensable for conducting business in the electronic healthcare field and are equally vulnerable. They are vulnerable because the electronic environments allow remote usage of records. In this regard, effective security systems are needed to limit unauthorized access to electronic patient records.
Electronic medical records are being commonly used and provide many benefits. Firstly, an electronic medical record improves the quality of healthcare and access to information. Secondly, it reduces clinical errors often attributed to illegible physician’ handwriting. Electronic medical records may also contribute to cost reduction measures in the management of patient records. Besides, they also improve information sharing by health practitioners thus enhancing communication of patient information.
Despite their benefits, electronic medical records present a number of challenges.
- They are costly and need a substantial amount of finance in order to set up.
- Electronic medical records are technical in nature; and demand training before they can be used.
- They lack standardized terminology and system architecture which render it hard to implement.
- Some of the challenges of using electronic medical records are security related.Security lapses might compromise the privacy and confidentiality of medical records.
Medical records are important ingredient in the health institutions. However, medical records need proper management through proper storage areas, controlled access and adequate preservation measures to improve efficiency, safety and quality of care. Thus, the reason why MediChain is here.
What is MEDICHAIN?
Medichain gives patients ownership of their own medical data. Medichain is a medical big-data platform. It allows patients to store their own data in a secure way and give access to specialists anywhere regardless of the payer network or EMR (Electronic Medical Record) used.
Medichain is a Medical Big-Data Platform. Our proposed system allows patients to store their own data off-chain in an appropriate geographic domain, and give access to doctors and specialists anywhere, regardless of the payer network or EMR used. Patients, doctors, and hospitals could put data into a compliant cloud which becomes part of the medichain ecosystem and the blockchain stores pointers and rules on usage and anonymity, while the data itself is stored off-chain in a compliant cloud, By improving patient data sharing and availability, and being open to add to any existing system or be managed automatically by doctor or by patient, medichain aims to allow better conditions for all parties, creating a better way of handling patient data than anything available today.
The Problems medicine in any country :
- Big spends Money on a year for research.
- Medical Errors data are now the 3rd largest cause of death and the coast very high
We have Solution about this problems :
By Using Blockchain Technology MediChain will promote these research breakthroughs and patients opting in and sharing their medical data, they will be able to help people who are suffering from similar health issues. Additionally, sharing medical data will streamline the process of finding cures to the world’s worst diseases.
Advantage of Medichain
- The User Member can Take data Anywhere and move it between healthcare provide, specialist, insuresrs.
- Keep data safe & anonymised and medical data is very confidential
- No cost for patient or doctors, moneestied by paatiens opting to let medical scientist and companies use data for reserch.
Token Holder Benefits
Medichain Utility Tokens (MCU) represent the value of arbitrary patient data blocks. MCU Utility tokens can be purchased via the platform during the tokens sale. Over time this value is adjusted for token availability, different data types, diseases, patient demographics etc., to reflect the buyer’s market.
- Any/All additional future business transactions on the MediChain Platform
- Research Program Voting. Get the chance to determine the focus of future research
- Personal Medical Data Storage and transfer
- Personal Medical Data Services
- MCU Discounts
How MediChain will work
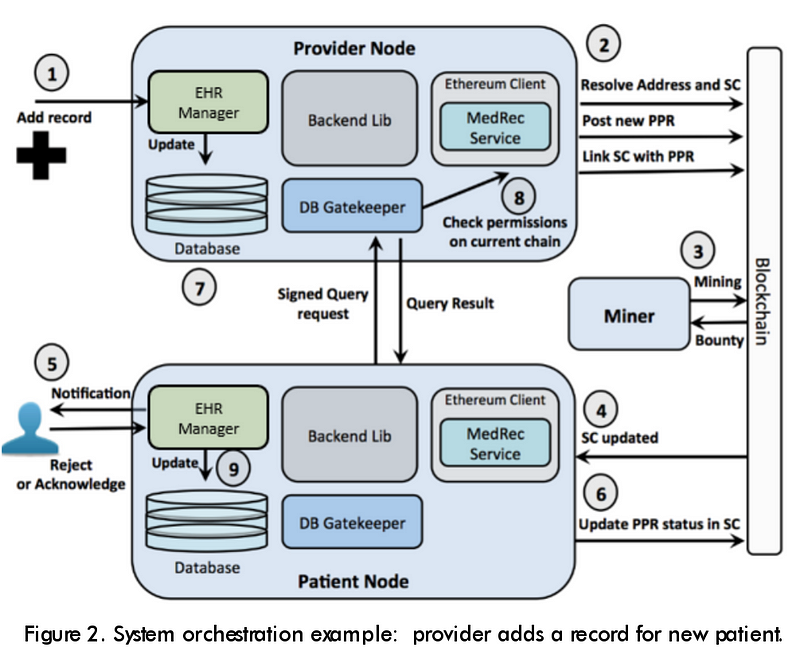
Any provider backend and user interface implementations can participate in the system by employing the modular interoperability protocol as defined through our blockchain contracts. Steps 1 and 2 in Figure 2 illustrate our backend implementation of a scenario where a provider adds a record for a new patient. Steps 4 to 6 in Figure 2 continue the use case described above from the patient node perspective. The patient’s modified Ethereum client continuously monitors her SC. Steps 7 to 9 in Figure 2 illustrate how a patient retrieves personal data from the provider node.
Other anticipated MediChain Network Development includes:
1. Diagnostic Tools
2. Related Algorithms
3. Personal Monitoring
4. Academic Medical Studies
5. Insurance Insurance Insurance (SmartCard Integration at this stage is introduced)
6. Integration of EMR (Electronic Medical Records)
7. Telemedicine
8 National Resource
1. Diagnostic Tools
2. Related Algorithms
3. Personal Monitoring
4. Academic Medical Studies
5. Insurance Insurance Insurance (SmartCard Integration at this stage is introduced)
6. Integration of EMR (Electronic Medical Records)
7. Telemedicine
8 National Resource
Token Holder Benefits
- Institutional Medical Data Services (including Diagnosis)
- Medical Research Data Services
- Any/All additional future business transactions on the MediChain Platform
- Research Program Voting. Get the chance to determine the focus of future research
- Personal Medical Data Storage and transfer
- Personal Medical Data Services
- MCU Discounts
Social Benefit
Population-based de-identified patient data has already produced advances against WHO top ten diseases such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and heart failure. Population data lets researchers tackle the big issues in medicine. By patients opting in and sharing their data, they promote the research breakthroughs that can one day improve their own health and help people who are suffering from similar health issues. Where there are commercial interests involved, such as drug development, the same applies, but pharmaceutical companies pay for the data and patients are paid for their contribution
What about emergency access to medical data in MediChain?
In an extended version of MediChain, information that is normally available to doctors in an emergency needs to be readily accessible even if the patient cannot give consent. Access needs to be customer defined with defaults consistent with current practice. It seems likely that most patients’ doctors will have access to the same level of records that they let them have now. Because there are multiple rules, the emergency services will have access to the level that the patient would normally grant them now (e.g. diagnostic levels). Neither of those levels would have mass access to raw data that might be useful to pharma or insurers and if necessary anonymity could be preserved while allowing access to the complete medical record.
What are the use of funds?
The funds are used to develop and promote the MediChain infrastructure and API and carry out the initial population of the chain with data which gives the chain market value. Promotion will be through wearable, desktop and kiosk devices including Apple Healthkit, Healmet Inc and through the Scripps Medical Research Center. A proportion of the development and promotion funds will be used to mature and integrate hardware used with the MediChain system including Smart Card ID systems and IoT devices.
Token Allocation
Total token : 100.000.000 MCU
Token Distribution
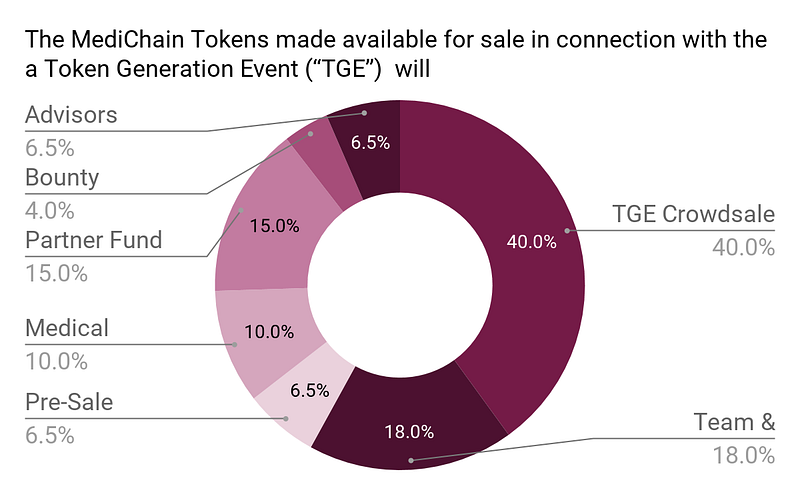
Pre-Sale 6,500,000 MCU
6.5% of MediChain tokens MCU will be distributed at presale
Public Main Sale 40,000,000 MCU
40% of MediChain tokens MCU will be sold through the public sale.
Medical Data Growth Fund 10,000,000 MCU
10% of tokens will be reserved for funding actions that add high-value medical data to the ecosystem through funding Research Grants
Partner Fund 15,000,000 MCU
15% of tokens will be reserved for future specialists and future rounds of investment, and distributed among future partners
Advisors 6,500,000
Bounty 4,000,000
1 MCU has a nominal release value of $1 US. All unsold tokens will be burned.
Let’s Join Token Sale
________________-Summary of MediChain ICO-________________
Solutions

Figure: How the Tokens are Used

Road Map 2018–2020
Q1 2018
- General MVP
- The MedRec system is live and scaled on the rackspace server
- Research
- Scientific program, 10+ rolling grant gets high quality data
- Pharma
- Outreach program to determine data needs
- Stakeholders
- Data stakeholder programs begin to ensure purchase
- HIPAA & FDA
- Compliance is complete
- Research
- Outreach programs 1–3 grants got the best data
- Team Growth
- Boost the world-class talent as needed
- Talent Search
- Interesting great talent. Includes hackathons
- Partner Creation
- Research and build high-value data
- Pharma
- The partnership develops 10–15 companies
Q2 2018
- Research
- Scientist Program, 3–5 grants to get high value data
- EHR / EMR
- The integration between EMR and MediChain is complete
- Analysis
- Analysis of ongoing operational needs
Q3 2018
- Large data
- 1TB + Data. Tech upgrade to handle the next petabyte
- Security
Q3: White hat team and additional tiger
- Technology
- Shift to accelerate parallel barriers for different WHO data sets
Q4 2018
- Large data
- PB + Data. Tech Upgrade to handle the next exabyte
- Strategic Review
- Maximize growth, value and social impact
- Talent Development
- Funnel, bring and develop the best talent
Q1 2019
- Research
- Scientific program, 5–10 grants get high value data
- API development
- Develop APIs for third party integration, promotion and support
- Data Hackathons
- Promote high-profile medical hackathons
Q2 2019
- Pharma
- The partnership closes with 5–10 companies
- Partner Creation
- Research and build high-value data
- Publication
- Target for first publication with epidemiology
Q3 2019
- Standard
- Establishment of the Medical Blockchain standard group
- Large data
- Tech EB + Upgrade to handle the next 10EB
- Pharma
- The partnership closes with 1–3 companies
Q4 2019
- Symposium
- IT Symposium & Annual Information Science for MediChain
- Technology
- Upgrade to version 2.0 for scale and security
- EHR / EMR
- The system starts getting patient data to MediChain
Q1 2020
- Smart card
- Initiation of the Doctor and Patient Smartcard program
Q2 2020
- Strategic Review
- Maximize growth, value and social impact
Q3 2020
- Large data
- Data 10EB +. Tech Upgrade to handle the next stage
Q4 2020
- Symposium
- Aims to be the leading data provider in the industry
- Pharma
- The partnership closes with 10–20 companies

Our Team
A diverse group of individuals brought together by a passion for the positive social potential of blockchain technology.


Our Advisors


For more information visit :
- Website : https://medichain.online
- Whitepaper:- https://docs.google.com/document/d/1M4j-ertE4Couj0tdVzNQeE_y3YgXZbJXAafiPO_v5C8/
- Telegram Group :- https://t.me/medichainonline_group
- Facebook:- https://www.facebook.com/MediChain.Online/
- Twitter :- https://twitter.com/MediChainOnline
- Linkedin :- https://www.linkedin.com/company/11419809/
- Bitcointalk ANN:- https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=2798374
Author
My Bitcointalk username: Liana Kurniawan










Komentar
Posting Komentar